|
| |
Issue no. 42 - September 1990
pdf
 version of this
Issue version of this
Issue
|
There is much information in this issue that is valuable
and useful. Online readers are reminded, however, that treatment guidelines and health
care practices change over time. If you are in doubt, please refer to
WHO's up-to-date Dehydration Treatment
Plans.
|
updated: 23 April, 2014
Pages 1-8 Dialogue on Diarrhoea Online Issue 42 -
September 1990
|
DDOnline Dialogue
on Diarrhoea Online Issue no. 42 September
1990 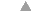 Page 1 2
Page 1 2
Drugs and childhood diarrhoea
Oral rehydration therapy should be the priority treatment for childhood diarrhoea.
Ninety five per cent of acute childhood diarrhoea, whatever the cause, can be successfully
treated with ORT and continued feeding, and does not require treatment with drugs. Despite
widespread promotion of this message, doctors continue to prescribe ineffective, expensive
and unnecessary drugs to treat diarrhoea; families continue to ask their doctors for them
or buy them over the counter from pharmacists; and manufacturers continue to promote and
market a wide range of anti-diarrhoeals. In many countries, drugs are used more than ORT
to treat diarrhoea (see="#page6">pages 6 and 7). On pages2, 3 and 4, DD reviews
some of the antibiotics most commonly used to treat diarrhoea, explaining why they are not
appropriate for acute diarrhoea in children. The next two issues will include reviews of
antimotility drugs and adsorbents. Unnecessary prescribing
Unnecessary prescribing has several important disadvantages. First, giving powerful
drugs to small children does not stop the diarrhoea, may cause dangerous side effects and
can result in families neglecting to rehydrate and feed a sick child. Second, drugs are
expensive for families and for the health system. The resources saved by reducing
unnecessary prescribing could-be better-used in other ways and the drugs saved for when
they are really needed. Third, in some countries, widespread use of antimicrobials has led
to high levels of antibiotic resistance - this means that the antibiotics are no longer
effective. On="#page5">page 5, DD describes how antibiotic
resistance develops and why it is a serious problem. Working together To reduce inappropriate use of drugs for diarrhoea, a co-ordinated response is needed.
This involves legislation, training and education of doctors and the public, and ensuring
that messages about drug treatment for diarrhoea are consistent. The article on="#page7">page 7 describes the coordinated approach being taken in Peru, where the
Ministry of Health, health professionals and activists are working together to tackle the
problem of widespread over-use of anti-diarrhoeal drugs in children. KME, WAMC and KA
|
In this issue:
- Drug reviews and resources
- Antibiotic resistance
- Reports from Peru, Pakistan and Indonesia
|
|
DDOnline Dialogue
on Diarrhoea Online Issue no. 42 September
1990  1 Page 2 3 1 Page 2 3
In most cases of childhood diarrhoea, drugs are unnecessary and
inappropriate. The WHO CDD programme has reviewed the literature on the efficacy and side
effects of the most widely used drugs. In this issue DD previews the information
available on three types of antimicrobial agents - neomycin, streptomycin and
hydroxyquinolines. Neomycin
Neomycin, an antibiotic contained in many oral anti-diarrhoeal preparations, has not
been proved to be effective in the treatment of acute diarrhoea. Neomycin given by mouth
has been associated with toxic effects on the gut and may worsen or prolong diarrhoea.
Widespread use of antibiotics such as neomycin can increase antimicrobial resistance. Oral
preparations containing neomycin are not recommended for use in the treatment of
diarrhoea. Formulations Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used either alone or in combination with
intestinal adsorbents, antimotility agents, or other antibiotics*. Pharmacology Neomycin is classified as non-absorbable - most of a dose given by mouth is excreted
unchanged in the stool, although some absorption does occur in the gastrointestinal tract.
What is absorbed is primarily excreted in the urine. How it works Neomycin is rapidly bactericidal (it kills and inhibits reproduction of bacteria
quickly). It is active against most aerobic Gram-negative organisms (see box below) and
staphylococci, but resistant strains of Escherichia colt, Klebsiella, Proteus,
Shigella, and Salmonella are common. Streptococci and Gram-positive bacilli are also
largely resistant. The mechanism of resistance of Gram-negative organisms to neomycin can also confer
resistance to other antibiotics (see="#page5">page 5). These resistance
factors, which can be transferred between bacteria, can sometimes also convey the ability
to produce enterotoxin. Widespread use of neomycin may therefore not only increase the
frequency of antibiotic resistant microorganisms, but may also help bacteria that cause
diarrhoea through enterotoxin to survive and spread.
- Diarrhoea can be caused by:
- Viruses - mostly rotavirus
- Bacteria - virtually all are Gram-negative aerobic pathogens
- Protozoa - especially Cryptosporidia, Giardia and amoeba
- Antibiotics are, in general, only useful for bacteria. They are
ineffective for viruses and have very limited value for protozoa, e. g. tetracycline is
partly effective for amoeba. There are, however, anti-protozoals for amoeba and Giardia.
- Antibiotics are ineffective for many food poisoning Salmonella.
They are not practical for other bacterial diarrhoeas, except cholera and shigellosis,
because one cannot determine clinically what bacterium is involved, if any, and thus what
antibiotic to give.
|
Efficacy Studies of neomycin in acute diarrhoea (of unknown aetiology) have reported 'cure'
rates ranging from 50-100 per cent. However, none included placebo controls, and since
most acute diarrhoeas are self-limiting, these reports of 'cures' are not meaningful. One double blind, placebo-controlled trial (see box,="#page4">page 4) of
neomycin in acute diarrhoea indicated that neomycin may actually increase the severity and
prolong the duration of the disease. There are no reported trials assessing neomycin in
the treatment of diarrhoea caused by enterotoxigenic , entero-adherent, enterohaemorrhagic
or entero-invasive E. coli. Some uncontrolled clinical observations have reported
good response of EPEC infections to neomycin therapy, but others have noted little
difference between neomycin and supportive therapy alone. The role of some antibiotics in treating shigellosis is well established, but not all
antibiotics are equally effective. Some early uncontrolled studies reported good results
from treating shigellosis with oral aminoglycosides. Others showed bacterial and clinical
cure rates of less than 50 per cent, and two suggested that streptomycin and neomycin were
no better in shigellosis therapy than simple supportive care. A double blind trial
comparing neomycin with ampicillin provided further evidence of the ineffectiveness of
non-absorbable antibiotics such as neomycin in shigellosis treatment. Studies have also shown that antibiotic therapy can actually prolong the carrier state
in Salmonella gastroenteritis, and clinical relapse may be more frequent in patients
treated with antibiotics. Placebo controlled trials of neomycin, ampicillin, and
amoxycillin have confirmed that these antibiotics are ineffective in treating Salmonella
gastroenteritis. Adverse effects Neomycin can damage the structure of the gut and interfere with its normal function. It
can cause malabsorption of fats, sugars and calcium. After as little as three days,
destruction of the microvilli lining the surface of the small intestine can appear; and
after seven days, invasion of the submucosal layer of the small bowel by eosinophilic
white cells has been observed. Controlled trials have demonstrated that extended courses
of neomycin prolonged the duration of diarrhoea. When given by injection, aminoglycosides are known to produce toxic effects on the
kidneys and ears. Because neomycin is usually given by mouth in diarrhoea treatment and is
poorly absorbed, these complications are uncommon, but there have been reports of toxic
effects with prolonged therapy or high doses, especially when kidney function is already
impaired. Formulations and drug interactions
Neomycin is usually sold in combination with a variety of adsorbents or other
antibiotics. None of these combination products has been shown to be effective in clinical
trials. The hydroxyquinolines contained in many of them have been withdrawn and prohibited
in many countries because of their dangerous effect on the nervous system, while kaolin
and pectin components can interfere with the absorption of certain useful antibiotics and
anti-malarials. *With all drug preparations it is important to look carefully at the contents or
ingredients as well as the brand name. Source: the text on pages="#page2">2 to 4 has
been adapted by DD from draft material prepared by the Control of Diarrhoeal
Diseases Programme of the World Health Organization (WHO). A series of nine reviews is in
preparation covering drugs commonly used in the treatment of diarrhoea. They will be
grouped in three sections: antimicrobials, antimotility drugs and adsorbents, and
published together as a WHO publication entitled The rational use of drugs in the
management of acute diarrhoea in children, to be available early in 1991 from:
CDD/WHO, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland.
|
|
DDOnline Dialogue
on Diarrhoea Online Issue no. 42 September
1990  2 Page 3 4 2 Page 3 4
Streptomycin
Streptomycin (or dihydrostreptomycin) has no proven value in the treatment of any
diarrhoea. It may increase the severity or prolong the duration of some cases of
diarrhoea. The widespread use of antibiotics such as streptomycin promotes resistance to a
variety of antimicrobial agents. Streptomycin (and dihydrostreptomycin) are not
recommended for the treatment of diarrhoea. Formulations Streptomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic which is important in tuberculosis (given
by injection), but which is also widely marketed as an oral preparation for diarrhoea
treatment. It is often combined with a variety of adsorbents, vitamins, or other
antibiotics. Dihydrostreptomycin is a related antibiotic with similar properties but
greater toxicity. Despite the absence of studies on its efficacy in diarrhoea, it is also
widely marketed as a diarrhoea treatment. Pharmacology Streptomycin is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, except when the mucosa is
damaged. Most of the drug is excreted unchanged in the stool. How it works Like neomycin, streptomycin kills and inhibits reproduction of many bacteria quickly.
Streptomycin is extremely useful in the treatment of tuberculosis. It is also active
against aerobic Gram-negative bacteria and some strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Extensive
use of streptomycin to treat other infections is associated with the development of
widespread antimicrobial resistance. Current reports of streptomycin resistance range from
36 per cent for Escherichia coli and 67 per cent for Shigella in Boston, USA, to
almost 100 per cent for enteropathogenic E. coli in New Delhi, India. As with
neomycin, widespread use may also lead to selection of organisms with enhanced
pathogenicity . Efficacy Most trials to assess the efficacy of oral streptomycin in the treatment of acute
diarrhoea have been uncontrolled, hence the results are not useful. In one controlled
trial, streptomycin therapy was associated with increased severity and duration of
diarrhoea.
|
Families and health workers need to know that ORT, not drugs,
should be given for most childhood diarrhoea.
Despite the lack of evidence of efficacy from controlled clinical trials, streptomycin
was widely used in the 1950s to treat diarrhoea due to Escherichia coli. Since the
emergence of widespread resistance, other antibiotics have been used to treat E. coli infections.
|
 |
Early uncontrolled trials suggested that streptomycin might be effective to treat
shigellosis; but other reports showed high failure rates or detected no difference between
streptomycin and supportive therapy alone. Some treatment failures have been attributed to
high rates of microbial resistance, but failure rates of 60 per cent in the treatment of
Shigella dysentery have been noted even when the infecting organisms are sensitive to
streptomycin when tested in the laboratory. Comparison of ampicillin and neomycin suggest that non-absorbable antibiotics*, such as
neomycin and streptomycin, do not have much effect on organisms that invade the intestinal
mucosa, and hence are of little use in treating Shigella infections. (* It is
better to use an absorbable antibiotic - one that can get into the blood and tissues.) High failure rates have also been reported with streptomycin in the treatment of
Salmonella gastroenteritis. Antibiotic therapy alone can actually prolong the carrier
state in acute gastroenteritis due to salmonella. (In contrast, Salmonella typhae, the
organism that causes typhoid fever, requires appropriate antibiotic treatment. Typhoid
fever is not normally associated with diarrhoea.) Adverse effects Streptomycin, like neomycin, if given by injection, may have toxic effects on the ears
and kidneys. If given orally, these complications are unlikely, but the extent of drug
absorption, and its toxicity in children with acute diarrhoea, have not been fully
evaluated. Formulations and drug interactions For diarrhoea treatment, streptomycin is usually sold in combination with other
ingredients such as kaolin, pectin, hydroxyquinolines, sulphonamides, or chloramphenicol.
These combination products have not been shown to be effective and the multiple agents
they contain cause additional side effects or undesirable drug interactions.
|
|
DDOnline Dialogue
on Diarrhoea Online Issue no. 42 September
1990  3 Page 4 5 3 Page 4 5
Hydroxyquinolines
Hydroxyquinolines are useful in the treatment of some parasitic infections. They
are, however, widely used for the routine treatment of diarrhoea, even though they have
not been shown to be effective. They have some effect on amoebic dysentery, but must be
used with other drugs to obtain satisfactory results. Side effects include severe eye and
nervous system disorders. Hydroxyquinolines are not recommended for diarrhoea because they
are ineffective and toxic: they are no longer used at all in developed countries. For
amoebic dysentery, less toxic, more effective amoebicides are available and are much
preferred. Formulations A range of products is available, the most popular being clioquinol
(iodochlorhydroxyquinoline) and iodoquinol (di-iodohydroxyquinoline); also
dibromohydroxyquinol (broxyquinoline) and chlorquinaldol (dichloromethylhydroxyquinoline).
These are sold under various trade names, either alone or combined with vitamins,
antibiotics or other agents. Pharmacology Hydroxyquinolines are well absorbed by the body. Though most of the drug is excreted in
the stools, up to 25 per cent of an oral dose is broken down in the liver and can be
recovered in the urine. How they work The way in which hydroxyquinolines work is unknown. They are active against both motile
and cyst forms of amoeba. They have also been shown to be active against a number of
enteric bacteria in the laboratory, but their effect on the bacteria within the gut is not
well understood. Efficacy Hydroxyquinolines function only within the intestinal lumen. When used alone to treat
amoebic dysentery, failure rates are high; in combination with antibiotics such as
tetracycline or erythromycin, treatment seems to be more successful, although most of
these antibiotics are not amoebicidal, and the rationale for combination therapy is
therefore unclear. No well-controlled trials have compared these combinations with
metronidazole, the current treatment standard for amoebiasis. Hydroxyquinolines have also been advocated to treat asymptomatic amoebic cyst passers,
but failure rates of up to 25 per cent have been seen and therapy for up to three weeks is
usually needed. Metronidazole produces comparable cure rates after only ten days of
treatment. However, therapy for asymptomatic cyst passers is not recommended because most
are colonised with non-pathogenic E. histolytica and up to 90 per cent of
infections terminate spontaneously without treatment. Moreover, in areas of high
endemicity, the probability of reinfection is high. With nitroimidazoles such as metronidazole (now available as a low cost generic),
tinidazole, ornidazole and nimorazole widely available, hydroxyquinolines are not needed
to treat amoebic diseases. Hydroxyquinolines are still used widely and non-selectively in acute diarrhoea, even
though no studies have shown them to be effective. The results of different trials give no
basis for recommending hydroxyquinolines for prevention or treatment of traveller's
diarrhoea or other diarrhoeas Adverse effects
Adverse effects include abdominal discomfort, diarrhoea, skin rash, acne, headaches and
enlargement of the thyroid gland. More serious are the many reports of neurological
complications linked to hydroxyquinolines. Between 1955 and 1970, about 10,000 cases of
subacute optic neuropathy (SMON) were diagnosed in Japan: five per cent of affected
persons died and up to 15 per cent were left completely disabled; 75 per cent of the cases
were associated with taking clioquinol. SMON is characterised by abdominal pain or
diarrhoea followed by painful sensations in the arms and legs and impaired vision. Removal
of clioquinol from the Japanese market led to a dramatic fall in the number of cases of
SMON. Similar neurological disorders associated with hydroxyquinolines have been reported
from Europe, the USA, Australia and India.
How do we know if a drug really works?
Drugs need to be tested objectively; the proper way to do this is a 'controlled
clinical trial'. The steps are as follows:
- Define the patients to be treated, making sure that they have the disease for which they
are to be treated, not some other illness.
- Randomly allocate patients to two (or more) treatment groups.
- It is best if treatments are given 'blind', i. e. neither the patients nor the health
workers know which treatment is given to specific individuals. This is called a 'double
blind' clinical trial.
- Assess recovery by objective measurements (such as duration of symptoms, amount of stool
passed, etc.) rather than because patients say they 'feel better'.
- If there is no effective treatment for the illness, test the new drug against a
'placebo' (an inert substance, with no pharmacological action, but which looks like the
treatment drug).
- If a recognised effective drug exists and the trial is to see whether a new product is
better, the standard and new drugs should be compared with each other in a 'double blind'
assessment.
- Assess the results of the two groups (standard treatment or placebo versus new
treatment) statistically, to see whether any difference in outcome is likely to be caused
by the drug, and not to have occurred by chance.
- Unless trials of drugs are done following these rules, it is not likely that their
results will be valid.
|
References for the studies referred to in these reviews are
available from DD/AHRTAG and CDD/WHO.
|
|
DDOnline Dialogue
on Diarrhoea Online Issue no. 42 September
1990  4 Page 5 6 4 Page 5 6
Antibiotic resistance
Q
What is an antibiotic?
A Antibiotics
are drugs that prevent or restrict bacterial growth, and so they are useful in treating
infections caused by bacteria. Some antibiotics have a 'broad spectrum' of action, that is
they work against a wide variety of micro-organisms. Others work only against specific
groups of organisms, and are not effective against others. This is because many bacteria
are naturally insensitive to some antibiotics. Antibiotics have no effect on viral
infections such as rotavirus diarrhoea.
Q When should antibiotics be given for diarrhoea?
A Antibiotics
are useful for diarrhoea treatment if there is blood in the stool, indicating that
Shigella is the likely cause; or cholera (diarrhoea caused by Vibrio cholerae) is
suspected: the patient has severe dehydration due to watery diarrhoea, is over two years
old, and cholera is known to be occurring in the area. Antibiotics should never be given
routinely for diarrhoea: they can be harmful, especially in young children, and may
prolong an episode of diarrhoea.
Q What is antibiotic resistance?
A Bacteria
that were originally sensitive to an antibiotic may become resistant to it. Resistance can
be demonstrated in the laboratory, but may also be seen clinically because the antibiotic
will have little or no beneficial effect on the illness.
Q Why is antibiotic resistance important?
A
If bacteria become resistant to particular antibiotics, then those drugs will be
ineffective - they will no longer treat the infection caused by the bacteria. Because of
this, some antibiotics are no longer useful in many parts of the world. Newer antibiotics
which are effective may not be available, or may be very expensive. Some strains of
bacteria have adapted to new antibiotics almost as soon as they become available, thus
greatly limiting their usefulness. In many countries, most E. coli bacteria are
resistant to cotrimoxazole, tetracyclines and other antimicrobials; and most Shigella to
ampicillin.
Q How does resistance develop?
A
There are two main ways in which bacteria can resist the effects of antibiotics. 1. The bacteria themselves can change so that antibiotics
are no longer effective against them - they become drug-tolerant. Because bacteria
reproduce rapidly they are very adaptable and able to change fast in order to survive.
When antibiotics are given, the more sensitive bacteria are rapidly eliminated, but if a
few adapt and become resistant, these will reproduce and soon replace the ones that were
sensitive. 2. The bacteria can develop ways to reduce the
effectiveness of the antibiotics - they become drug-destroying. For example,
bacteria can produce substances which inhibit the action of some antibiotics e. g.
betalactamases which make penicillins ineffective, and cephalosporinases or
aminoglycoside-inactivating enzymes which make cephalosporin antibiotics (gentamicin and
kanamycin) ineffective. Resistance is more likely to develop if antibiotics are widely and frequently used; and
antibiotics are used in doses which are not large enough or are used for too short a time,
so that not all the disease-causing bacteria are destroyed. Antibiotic resistance often develops because a bacterium acquires a component known as
a plasmid. A bacterium which is resistant to an antibiotic because it possesses a
resistance factor (R-factor) can pass this on, by means of a plasmid, to a bacterium which
was previously sensitive to the antibiotic. The plasmid contains genetic material which is
transferred from one bacterium to another. If antibiotics are used after a resistant
strain develops, that strain survives, continues to multiply and can quickly become
predominant.
Q What can be done to prevent resistance from developing?
A
The correct use of antibiotics is extremely important. Antibiotics should never be used
when they are not needed, because resistance becomes more likely if a drug is used more
widely. Antibiotics should always be taken in the right doses and for the recommended
amount of time. If a drug is prescribed to be taken for five days, it is important to
continue taking it for five days. Often a patient may begin to feel better and symptoms
may be lessened in only two or three days, but the bacteria are unlikely to have been
fully eliminated in this time. Stopping the drug early helps resistance to develop, and
symptoms may return because the bacteria are able to grow again. Often, people will be
tempted to take less than the recommended amount of a drug if it is cheaper for them to
buy less, and they do not understand why a full course is needed.
What the patient can do:
- remember that ORT is the correct treatment for most diarrhoea;
- never use antibiotics for diarrhoea unless they are prescribed by a doctor or health
worker, never give anti-diarrhoeal drugs to children or infants;
- if an antibiotic is prescribed, be certain you understand the instructions for its use
and follow them carefully: take it for the recommended time, and do not stop even if the
symptoms clear up;
- never try to save money by buying less than the prescribed amount.
What the doctor can do:
- never prescribe antibiotics or antibacterial agents unless they are absolutely
necessary; for diarrhoea, give antibiotics only for dysentery or when cholera is
suspected;
- explain to the patient that they must complete the full course of treatment, even though
the symptoms may go away or become less before the end of the treatment.
What the health authority can do:
- do not allow 'prescription only' medicines (such as antibiotics) to be sold without a
prescription;
- ensure that antibiotics are only prescribed by trained health workers, and that advice
is given on their use;
- ensure that drug legislation is adequate and that it is enforced;
- as part of the strategy to control diarrhoeal disease, make sure that ORT is promoted as
the best and most important treatment for diarrhoea.
|
With thanks to Professor P D'Arcy, The School of Pharmacy, University
of London, 29/39 Brunswick Square, London WC1N 1AX, UK.
|
|
DDOnline Dialogue
on Diarrhoea Online Issue no. 42 September
1990  5 Page 6 7 5 Page 6 7
PAKISTAN Should ORS be marketed like other drugs? Why do people use 'anti-diarrhoeal' drugs
when ORS is better and cheaper? Camille Saade and Maggie
Huff-Rousselle argue that understanding commercial sales techniques could
help to increase the use of ORS. Commercial marketing is a powerful force. It is, for example, a factor in persuading
women to use powdered milks and infant formulas instead of breastfeeding. To promote ORT
successfully, it is essential to understand the commercial forces used to promote the
drugs which are often used instead of ORT. Figure 1 shows the
results of a study in Pakistan (carried out by the PRITECH project) on the market for
commercial treatments for diarrhoea. It is estimated that at least US$ 7.5 million is
spent on these products each year, with only about nine per cent of this spent on ORS
packets (of which eight different brands are available). Over 90 per cent of the total was
spent on 'anti-diarrhoeal' drugs which are ineffective and potentially dangerous. As well
as the 82 different combination drugs which include antibiotics in their formula, this 90
per cent share included motility inhibiting drugs and intestinal adsorbents such as
combinations of kaolin and pectin.
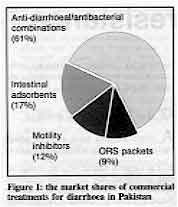 |
Figure 1: the market shares of
commercial treatments for diarrhoea in Pakistan The best-selling 'anti-diarrhoeal' drugs in Pakistan are all produced by subsidiaries
of multinational companies with tremendous marketing strength and experience. The main
marketing technique in Pakistan is 'detailing', which involves members of the 50 to 80
person sales force of each company making regular visits to most doctors in the country.
|
Before and during the diarrhoea season, company representatives increase the emphasis
on 'anti-diarrhoeal' drugs by handing out promotional literature and free samples. This
activity is backed up by advertising in medical journals and by techniques aimed at
pharmacists: giving free goods, bonus offers and sales incentives. Only one company carried out promotion of ORS . This company was responsible for 80 per
cent of ORS sales, and employed 41 'detailmen' to visit doctors. In urban areas, company
staff visited drug retailers and wholesalers to encourage orders for ORS packets, as well
as to promote ORS by talking to doctors. In rural areas, a further 120 sales staff worked
with a network of regional distributors, and also with paramedical workers. The relatively weak market position of ORS may be one reason why it is not used more
often. In many places, increased marketing of ORS might help to increase both its sales
and use. Health workers and others concerned with public health can also take action.
Those targeted by representatives promoting 'anti-diarrhoeal' drugs must understand that
these drugs are promoted to increase sales, not necessarily because they have proven value
for treating diarrhoea. This is especially important because 'anti-diarrhoeal' drugs are
potentially dangerous. Also their high costs waste health service resources, and the
over-use of antibiotics encourages the development of resistant strains of bacteria. Those
involved in marketing of ORS need to analyse the competition in the commercial sector, and
develop strategies to increase the demand for ORS. Camille Saade, AED, PRITECH Project, Washington DC, USA; and Maggie Huff-Rousselle,
Initiatives Inc, 239 Commonwealth Avenue, Boston, MA 02116, USA.
INDONESIA
Drug prescribing for diarrhoea In 1987 the Ministry of Health (with support from USAID) began a study of drug
selection and procurement procedures for health facilities. Part of the study looked at
the prescribing of drugs in 4,060 cases of childhood illness, including diarrhoea. The
results of the study (1) revealed that:
- nearly 60 per cent of all patients received prescriptions for four or more drugs;
- the average number of drugs per case for all diagnoses was 3.8, and one in four drugs
used was given by injection;
- 88 per cent of children under five were treated with an antibiotic, but the average
prescription was for only two days.
Specifically for diarrhoea treatment, the average number of drugs prescribed per case
was similar (4.0 for children under five, 3.8 for older children). Also:
- antibiotics were prescribed more than twice as often as ORS, and over 50 per cent of
cases that received an antibiotic were given two or more of these agents;
- more vitamins and minerals were prescribed than ORS.
1. Child Survival Pharmaceuticals of Indonesia, Part II (" CSP-II"),
1988. Jakarta, Ministry of Health. Source: WHO/CDD/ 90.34 Seventh Annual Report.
|
|
|
DDOnline Dialogue
on Diarrhoea Online Issue no. 42 September
1990  6 Page 7 8 6 Page 7 8
PERU
Co-ordinated national action
Inappropriate use of drugs for childhood diarrhoea is a major problem in Peru. Patricia
Paredes and Hildebrand Haak report on recent steps
taken to improve the situation. For ten years, the national Control of Diarrhoeal Diseases (CDD) Programme in Peru has
promoted oral rehydration therapy (ORT) for diarrhoea, and the use of a few selected
antimicrobials for dysentery only. National surveys have, however, found that ORT use is
still low, while the use of drugs for diarrhoea in children under five is very high.(1,2). To address the problem, a workshop was organised in Lima by scientific professionals
and the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) in collaboration with the Ministry of
Health. Health professionals, health administrators, international agencies, Peruvian
researchers, health activist groups and others attended, contributing much information on
drug use for childhood diarrhoea. Research findings Workshop participants presented results of research studies. Two national surveys
showed that, in 1984, 50 per cent, and in 1986, 62 per cent of all diarrhoeal episodes in
children under five were treated with some kind of drug. The drugs most frequently used
were antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, tetracycline, neomycin and cotrimoxazole, and
antimotility agents like loperamide (1,2). A study of beliefs and behaviour, conducted in
the outskirts of Lima in 1987-88, showed that traditional remedies were widely used for
diarrhoea, but that modem pharmaceuticals were often also used in combination with them.
 |
Many children in Peru are prescribed inappropriate drugs for
diarrhoea. Loperamide was the most widely used drug, followed by a combination tablet containing
chloramphenicol and tetracycline. These tablets can easily be bought without prescription
in local shops. Inappropriate drug use for diarrhoea is not just a result of so-called
'self-medication' by families. Doctors also frequently prescribe ineffective drugs. A
survey of patterns in drug prescribing found that, of patients attending a health facility
or a private surgery for diarrhoea treatment, 57 per cent received a prescription for
antibiotics, and 55 per cent for an 'anti-diarrhoeal' drug.(3).
|
Dangerous and expensive Most of the medicines described above are never appropriate for diarrhoea, and the
remainder are being greatly over-prescribed. Over-use of antibiotics increases the chances
of resistant bacterial strains developing, and drugs such as loperamide are dangerous and
may be fatal in young children. As well as being ineffective or harmful, such over-prescribing and over-use of drugs is
also extremely expensive. Data from the pharmaceutical industry show that between June
1988 and June 1989, approximately US$ 2.5 million was spent on drugs to treat diarrhoea.
Only 1.4 per cent of spending on rehydration solutions was on official ORS packets, which
are cheap and made according to the WHO formula. The rest was spent on more expensive
commercial preparations of glucose-electrolyte solutions, most of which differ
substantially from the approved formula.(3) During discussion of these data it became clear that inappropriate drug use is a
complex problem involving many interests. For example, even when mothers, pharmacists and
doctors are aware of ORT and correct diarrhoea management, they give a variety of reasons
for using other treatments which seem to them to be better. Although there is still no
safe treatment which stops the diarrhoea quickly, doctors will prescribe a remedy which
claims to give a rapid 'cure', because this is what the mother wants. However, there is
little awareness of the possible dangers of these drugs, of their unnecessary cost,
especially for poor families, and the role they play in delaying the use of effective
rehydration therapy. Action The workshop led to a series of actions.
- PAHO/ WHO published a report of the data and the discussion which has been
distributed within Peru and in the PAHO region.(3) The workshop is presented as an
example for other national programmes.(4)
- The Ministry of Health organised a series of paediatric forums throughout the
country where correct case management of diarrhoea and the disadvantages of
'anti-diarrhoeal' drugs were discussed with doctors, nurses, pharmacists and students.
- Messages about ORT and inappropriate drugs were reinforced through additional
teaching sessions and radio interviews.
- Inappropriate use of antibiotics and other drugs during diarrhoea is now recognised
as important by the Ministry of Health, and there are plans to focus on the problem in the
next update of the national diarrhoea treatment guidelines.
- A local health activists group, in collaboration with the Ministry of Health, has
organised several forums for medical and pharmaceutical students on inappropriate drug
use. This group has also prepared a popular information folder on 'anti-diarrhoeals',
which includes, among other printed materials, the workshop report and a WHO document on
proper case management of diarrhoea.
- The workshop report has also been used as a basis for discussion in regional
seminars of the National Pharmacists Association. The Association has recognised the
problem and is willing to collaborate in efforts to reduce the inappropriate dispensing of
pharmaceuticals for childhood diarrhoea.
Working together One strength of this effort has been the willingness of the scientific community, the
Ministry of Health, international agencies and health activist groups to work together and
recognise the seriousness of the problem. The positive attitude of those involved in
trying to find solutions, each in their own field and in collaboration with others,
deserves special attention and has been one of the most encouraging results of the initial
workshop. Dr Patricia Paredes, Instituto de Investigation Nutritional, Av. la Universidad S/N,
Apto 18-0191, Lima 18, Peru; and Dr Hildebrand Haak, PAHO/WHO, Lima, Peru. With thanks to
Dr Mary Penny, IIN Research Director. 1. ENNSA: INE: Informe General Peru 1986. pp 145-146.
2. ENNSA: INE: Informe General Peru 1988. pp 118-121.
3. Medicamentos inapropiados en diarrea: la magnitud del problema. PAHO/WHO, Lima,
1989.
4. Programme for Control of Diarrhoeal Diseases. Seventh Programme Report. WHO,
1988-1989.
|
|
DDOnline Dialogue
on Diarrhoea Online Issue no. 42 September
1990  7 Page 8 7 Page 8
 |
More information on drugs, including drugs for diarrhoea,
can be obtained from the organisations and publications listed below. |
- All India Drug Action Network (AIDAN). Contact: Voluntary Health Association of India,
40 Institutional Area, South of ITT, New Delhi 110016, India. AIDAN is a network of
health, consumer, legal aid, and human rights organisations.
- Drug Disease Doctor. Subscription. Published by Drug Action Forum, P 254, Block
B, Lake Town, Calcutta 700089, India. Quarterly journal on rational drug therapy and
prescribing practice.
- The Drug Monitor. Free. Published by the Health Action Information Network
(HAIN), 9 Cabanatuan Road, Philam Homes, Quezon City, Philippines.
- Drug Information. Free. Published by the Pharmaceuticals Unit, World Health
Organization, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland. A bulletin for the international transfer of
information on current drug topics.
- Essential Drugs Monitor. Free. Published by the World Health Organization, 1211
Geneva 27, Switzerland. The newsletter of the WHO Action Programme on Essential Drugs and
Vaccines.
- HAI News. Subscription. Published by Health Action International (HAI), IOCU, PO
Box 1045, 10830 Penang, Malaysia. Regional offices at HAI-Europe, Jacob van Lennepkade 334
T, 1053 NJ Amsterdam, Netherlands; and IOCU Regional Office for Latin America and the
Caribbean, Casilla 10993, Sucursal 2, Montevideo, Uruguay. The newsletter of HAI, a
network of consumer, development action and other public interest groups worldwide.
- INRUD News. Free. Published by the International Network for Rational Use of
Drugs, 165 Allandale Road, Boston, Massachusetts 02130, USA. INRUD is a co-operative
organisation of health workers, administrators and researchers in developing countries
aiming to improve drug use. There are several different national groups.
- WHO Drug Information. Subscription. Published in English and French by the World
Health Organization, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland. Journal of drug development and
regulation.
Further reading
- Chetley, A, 1987. Antibiotics: the wrong drugs for diarrhoea. Health Action
International. Available from HAI Europe.
- Cutting, W A M, 1989. Self-prescribing and promotion of anti-diarrhoeal drugs. Lancet
8646: 1080.
- Dean, P and Ebrahim, G J, 1986. Practical care of sick children: a manual for use in
small tropical hospitals. Macmillan, 348 pages.
- Ghai, O P, 1987. Understanding and managing acute diarrhoea in infants and young
children. All-India Inst of Medical Sciences, 25 pages.
- Laing, R O, 1990. Rational drug use: an unsolved problem. Tropical Doctor 20(3):
101-103. A short and recent overview.
- Merson, M H, 1987. Proper treatment of diarrhoea: role of the pharmacist. International
Pharmacy Journal 1: 52-56.
- Quinby Rush, C and White, K, 1988. Control of diarrhoeal diseases: an annotated
bibliography of PRITECH holdings. PRITECH, 333 pages.
- Rylance, G (ed), 1987. Drugs for children. Non-serial publication available from
WHO. 185 pages.
- Banned and Bannable Drugs, 1986 (third revised edition, 1989). The Voluntary
Health Association of India (VHAI), 40 Institutional Area, South of IIT, New Delhi 110016,
India. 106 pages. Available from VHAI.
- Drugs in the management of acute diarrhoea in infants and young children, 1989.
Bull. WHO 67(1): 94-96. A short overview. Based on the unpublished document
WHO/CDD/CMT/ 86.1 Rev 1 (1988).
- WHO, 1988. The use of essential drugs: third report of the WHO expert
committee. Technical report series 770. 63 pages. Includes a model list of essential drugs
designed for individual countries to use to develop their own lists.
- WHO, 1988. Essential drugs for primary health care: a manual for health workers in
South-East Asia. SEARO Regional Health Papers No 16, 105 pages. SwF10/ US$8, order no.
1580016.
- WHO, 1987. Use of drugs in the treatment of diarrhoea. CDD/TAG/87.5.
- WHO, 1987. The rational use of drugs. Report of the Conference of
Experts, Nairobi, 25-29 November 1985, 329 pages. SwF52/ US$ 41.60, order no. 1150271.
- WHO, 1988. The world drug situation. 123 pages. SwF20/ US$ 16.00.
|

Scientific editors Dr Katherine Elliott and Dr William Cutting
Managing editor Kathy Attawell
Assistant editor Nina Behrman Editorial advisory group
Professor J Assi Adou (Ivory Coast)
Professor A G Billoo (Pakistan)
Professor David Candy (UK)
Professor Richard Feachem (UK)
Dr Shanti Ghosh (India)
Dr Michael Gracey (Australia)
Dr Norbert Hirschhorn (USA)
Dr Claudio Lanata (Peru)
Professor Leonardo Mata (Costa Rica)
Dr Jon Rohde (USA)
Dr Mike Rowland (UK)
Ms E O Sullesta (Philippines)
Professor Andrew Tomkins (UK)
Dr Paul Vesin (France) With support from AID (USA), ODA (UK), UNICEF, WHO Publishing partners
BRAC (Bangladesh)
CMAI (India)
CMU (China)
Grupo CID (USA)
HLMC (Nepal)
lmajics (Pakistan)
ORANA (Senegal)
RUHSA (India)
Consultants at University Eduardo Mondlane (Mozambique)
|
Issue no. 42 September 1990
Page Navigation
This edition of Dialogue on Diarrhoea Online is produced by Rehydration Project. Dialogue on Diarrhoea was published four times a year in English, Chinese, French, Portuguese, Spanish, Tamil,
English/Urdu and Vietnamese and reached more than a quarter of a million readers worldwide. The English edition of Dialogue on Diarrhoea was produced and distributed by Healthlink Worldwide. Healthlink Worldwide is committed to strengthening primary health care and
community-based rehabilitation in the South by maximising the use and impact
of information, providing training and resources, and actively supporting
the capacity building of partner organisations. - ISSN 0950-0235 Reproducing articles
Healthlink Worldwide encourages the reproduction of
articles in this newsletter for non-profit making and educational uses. Please
clearly credit Healthlink Worldwide as the source and, if possible, send us a copy of any uses made of the material.
|
updated: 23 April, 2014
updated: 23 April, 2014
|